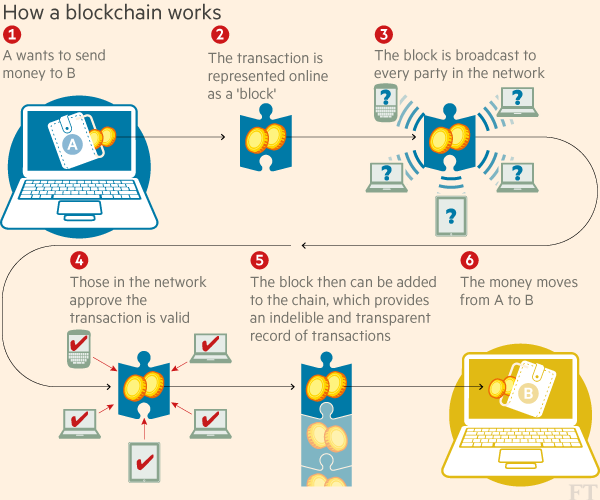
→ Blockchain is a decentralized, incorruptible digital ledger that can record transactions (like, but not limited to, financial transactions) directly among peers without having involvement of a third party or centralized system.
As an analogy, it can be thought of as a distributed database that maintains a shared list of records. These records are called blocks. Each encrypted block holds the history of blocks that came before it, with timestamped transaction data which chain the blocks together and hence termed as blockchain.
The blockchain is also called public ledger because it is openly available for everyone to read.
Its main characteristics are:
From <https://www.coindesk.com/information/what-is-a-distributed-ledger/>
As an analogy, it can be thought of as a distributed database that maintains a shared list of records. These records are called blocks. Each encrypted block holds the history of blocks that came before it, with timestamped transaction data which chain the blocks together and hence termed as blockchain.
The blockchain is also called public ledger because it is openly available for everyone to read.
Its main characteristics are:
- Decentralized peer to peer network
- Establishing trust among unknown peers
- Recording the transaction in immutable, distributed ledger
How is trust achieved?
- Validate, Verify and confirm transactions
- Record the transactions in a distributed ledger of blocks
- Create a tamper-proof chain of blocks
- Implement a consensus protocol for agreement on the block to be added in the chain
Distributed Ledger
In its simplest form, a distributed ledger is a database held and updated independently by each participant (or node) in a large network. The distribution is unique: records are not communicated to various nodes by a central authority but are instead independently constructed and held by every node. That is, every single node on the network processes every transaction, coming to its own conclusions and then voting on those conclusions to make certain the majority agree with the conclusions.
Once there is this consensus, the distributed ledger has been updated, and all nodes maintain their own identical copy of the ledger. This architecture allows for a new dexterity as a system of record that goes beyond being a simple database.
From <https://www.coindesk.com/information/what-is-a-distributed-ledger/>
No comments:
Post a Comment